
Publisher:
Bonnie King
CONTACT:
Newsroom@Salem-news.com
Advertising:
Adsales@Salem-news.com

~Truth~
~Justice~
~Peace~
TJP
Sep-25-2010 20:34

 TweetFollow @OregonNews
TweetFollow @OregonNews
Shorebird Researchers Document Red Knot's Record-breaking Non-stop Flight and Total Migration Distance
Salem-News.comThe study also found that the birds, most likely flying as part of a flock, took some previously unknown migratory paths.
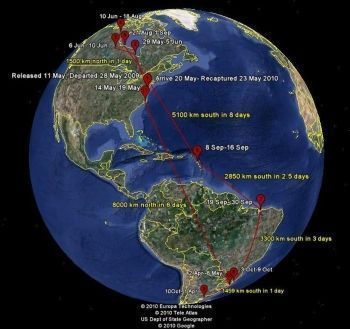 google earth view of flight path |
(TRENTON, NJ) - Researchers now know that this spring, a 6-ounce Red Knot (Calidris canutus)—a shorebird only two-thirds the size of a city pigeon—flew non-stop for six days and nights, covering 5,000 miles (8,000 kilometers) across the Amazon and the Atlantic Ocean between southern Brazil and North Carolina, shattering the previous known Red Knot record by nearly 700 miles. In late August 2009, the same Red Knot flew non-stop for eight days between Canada’s Hudson Bay and the Caribbean, a distance of 3,167 miles (5,100 kilometers).
These are just two of the fascinating results recently published in the bulletin of the International Wader Study Group by shorebird researchers from the United States, Canada, Argentina, Britain, and Australia. Lead author Dr. Larry Niles, a scientist with the Conserve Wildlife Foundation of New Jersey, and his colleagues employed a relatively new technique—sunrise- and sunset-sensitive geolocators attached to the legs of Red Knots in New Jersey—to shed new light on the annual migration of this species of special concern. Red Knots winter as far south as Tierra del Fuego, South America, and breed in the Arctic. Researchers also learned that the birds sometimes make extensive detours around tropical storms during their southbound migration and discovered new migratory paths.
In May 2009, geolocators were attached to the legs of 47 Red Knots captured during their annual stopover on the Delaware Bay (New Jersey, USA), where they “refuel” on horseshoe crab eggs prior to their final flights to Canadian Arctic breeding grounds. In May 2010, three of those birds were recaptured during their return to the Delaware Bay, and their geolocators were retrieved. Analyzing the year-long geolocator data, researchers now know that the same bird that flew nearly 5,000 miles non-stop for six days also covered one of the longest recorded distances in a year of any bird species: 16,600 miles (26,700 kilometers).
“We’ve long known that reaching the Arctic in time for breeding requires long-distance northbound flights, thereby making quality stopovers, such as Delaware Bay, so critical for resting and refueling,” says Niles, the project’s chief investigator. “The surprise here was that after the breeding season all three birds with geolocators also made long-distance return flights, highlighting the importance of southbound stopover sites such as Cape Cod in Massachusetts, and New Jersey’s Atlantic coast."
The data also revealed that during the 2009 southbound migration, tropical storms caused two of the birds to make long, energy-depleting detours. One bird detoured more than 620 miles (1,000 kilometers) to avoid Tropical Storm Danny in late August, and in early September encountered Tropical Storm Erica before arriving in Brazil. The other bird detoured approximately 870 miles (1,400 kilometers) to avoid strong adverse winds while over the Atlantic before resuming its flight south.
“Global warming models suggest increases in the frequency and strength of tropical storms,” says Niles. “If this happens it could be devastating to shorebirds’ southward migration.”
The study also found that the birds, most likely flying as part of a flock, took some previously unknown migratory paths. One flew straight across the Amazon, through habitat mostly inhospitable to shorebirds. The data not only re-validated the importance of a number of key, known stopovers (San Antonio Oeste in Argentina, the Maranhão region of northern Brazil, and the Delaware Bay in the U.S.), they also identified a number of previously little-known stopovers, such as the Churchill region of Hudson Bay and the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean.
These results suggest that geolocators are likely to afford valuable new insights to our understanding of Red Knot migration strategies, as well as their breeding and wintering locations. Biologist Patricia González is an Argentine researcher who follows the knots to many places along their migratory route. “There are no borders for these birds,” she says. “This kind of project is only possible thanks to the enthusiastic network of researchers, volunteers, and communities that is being built throughout the American flyway. The knots are teaching us about collaboration.”
Between May 2009 and May 2010, the research team fitted geolocators to 200 more Red Knots they caught in Canada, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Florida, Texas, and Argentina. The future recovery of some of these birds and their geolocator data will add even more knowledge to aid Red Knot conservation. "Red Knots have faced terrible population declines in the past ten years,” says Dr. Charles Duncan, Director of the Shorebird Recovery Project at the Manomet Center for Conservation Sciences. “The combination of new technologies in this exciting research with intensive conservation efforts makes us hopeful that, together, we can recover the populations of this amazing bird, one of the planet’s great travelers.”
About Conserve Wildlife Foundation of New Jersey: Conserve Wildlife Foundation is a statewide non-profit organization dedicated to the rare and imperiled species of wildlife that live and breed in, and migrate through New Jersey. Learn more about the foundation at www.conservewildlifenj.org.
About the Shorebird Recovery Project: Manomet Center for Conservation Sciences has played a leadership role in shorebird research and conservation for nearly 40 years. Its long-term commitment to understanding populations of shorebirds and the factors that affect them has revealed dramatic decreases for many species. Manomet’s Shorebird Recovery Project strives to rebuild populations with a three-pronged approach: (1) building the science foundation, (2) advancing site-based conservation, and (3) using explicit success measures to evaluate and demonstrate progress. Read more about this initiative at www.manomet.org/our-initiatives/shorebird-recovery-project
Articles for September 24, 2010 | Articles for September 25, 2010 | Articles for September 26, 2010

Quick Links
DINING
Willamette UniversityGoudy Commons Cafe
Dine on the Queen
Willamette Queen Sternwheeler
MUST SEE SALEM
Oregon Capitol ToursCapitol History Gateway
Willamette River Ride
Willamette Queen Sternwheeler
Historic Home Tours:
Deepwood Museum
The Bush House
Gaiety Hollow Garden
AUCTIONS - APPRAISALS
Auction Masters & AppraisalsCONSTRUCTION SERVICES
Roofing and ContractingSheridan, Ore.
ONLINE SHOPPING
Special Occasion DressesAdvertise with Salem-News
Contact:AdSales@Salem-News.com

Salem-News.com:
googlec507860f6901db00.html

Terms of Service | Privacy Policy
All comments and messages are approved by people and self promotional links or unacceptable comments are denied.
[Return to Top]
©2025 Salem-News.com. All opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Salem-News.com.